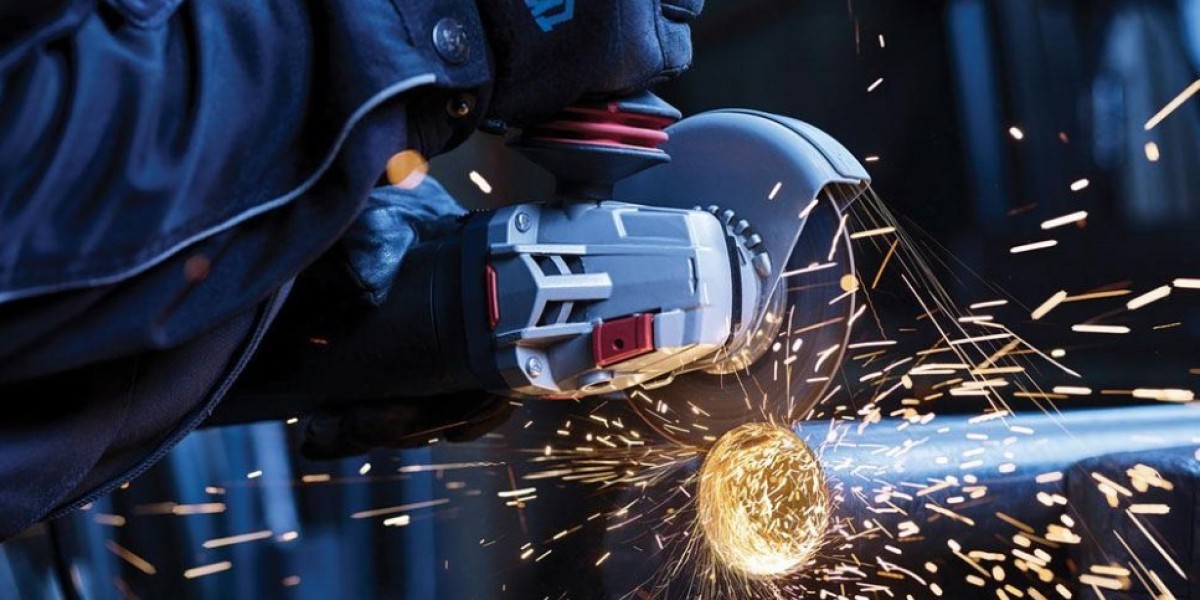
Abrasive wheels and cutting tools are among the most commonly used pieces of equipment on construction sites, yet they are also responsible for a high number of serious injuries. These tools operate at high speeds and can cause severe cuts, fractures, burns, and eye injuries if used incorrectly. Common risks include wheel breakage, kickback, contact with moving parts, and exposure to dust and sparks. Site personnel must understand that even minor misuse, such as incorrect mounting or excessive pressure, can lead to catastrophic failure. Developing a strong foundation in construction safety principles, such as those covered in a Health and Safety in a Construction Environment Course, helps workers recognise hazards early and adopt safer working behaviours before accidents occur.
Selecting the Correct Equipment for the Task
Safe operation begins with selecting the right abrasive wheel or cutting tool for the job. Different materials require specific wheel types, sizes, and speeds, and using the wrong combination can result in tool failure. For example, a wheel designed for metal cutting should never be used on masonry, and vice versa. Operators must check the manufacturer’s specifications, including maximum operating speed, compatibility, and intended use. Tools should also be inspected to ensure guards, handles, and safety features are intact. Proper selection reduces strain on equipment and lowers the risk of wheel shattering or tool malfunction. This step is often overlooked, yet it plays a critical role in preventing avoidable site injuries.
Pre-Use Inspection and Maintenance Practices
Before any abrasive wheel or cutting tool is used, a thorough pre-use inspection is essential. Workers should check for cracks, chips, uneven wear, or signs of damage on the wheel or blade. The “ring test” is commonly used for bonded abrasive wheels to identify internal cracks that may not be visible. Tools should also be examined for loose components, damaged cables, or faulty switches. Maintenance records should be kept up to date, ensuring tools are serviced according to manufacturer guidance. A poorly maintained tool increases the likelihood of sudden failure during operation. Regular inspections not only protect workers but also extend the lifespan of equipment and improve overall site efficiency.
Importance of Correct Mounting and Guarding
Correct mounting of abrasive wheels and cutting tools is a crucial safety requirement. Wheels must be securely fitted using the correct flanges and tightened according to manufacturer instructions. Over-tightening or improper alignment can cause stress fractures, leading to wheel disintegration during use. Guards must always be in place and adjusted to protect the operator from sparks, debris, and fragments in the event of breakage. Removing or bypassing guards significantly increases injury risk and is a common factor in serious accidents. Site supervisors should enforce strict rules around guarding, reinforcing that safety devices are not optional but essential components of safe tool operation.
Safe Operating Techniques on Site
Using correct operating techniques greatly reduces the risk of accidents when working with abrasive wheels and cutting tools. Operators should maintain a stable stance, keep both hands on the tool where applicable, and avoid awkward positions that could cause loss of control. Excessive force should never be applied; the tool should be allowed to cut at its own pace. Workers must also ensure they are not positioned in line with the wheel, reducing injury risk if the wheel breaks. Clear communication with nearby colleagues is essential to prevent accidental contact. Training and awareness, often reinforced through structured learning like a Health and Safety in a Construction Environment Course, help embed these safe practices into daily routines.
Personal Protective Equipment and Environmental Controls
Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in protecting site personnel when operating cutting tools. Eye protection is essential to guard against flying debris, while gloves can improve grip and reduce vibration exposure when appropriate. Hearing protection may be required due to high noise levels, and respiratory protection should be used when cutting materials that generate harmful dust. The work area should be well-lit, free from obstructions, and adequately ventilated. Flammable materials must be cleared away to reduce fire risk from sparks. PPE and environmental controls work together to create a safer operating environment and should never be considered a substitute for correct tool handling.
Training, Supervision, and Legal Responsibilities
Proper training and supervision are fundamental to the safe use of abrasive wheels and cutting tools. Only trained and authorised personnel should operate this equipment, as required by health and safety regulations. Training should cover tool selection, inspection, mounting, operation, and emergency procedures. Supervisors must monitor work practices and intervene if unsafe behaviour is observed. Employers have a legal duty to provide adequate instruction and ensure risk assessments are in place. Workers also share responsibility by following procedures and reporting defects. Ongoing education, supported by recognised courses, ensures that safety knowledge remains current and relevant in a constantly evolving construction environment.
Conclusion
Safe operation of abrasive wheels and cutting tools relies on a combination of correct equipment selection, thorough inspection, proper mounting, safe techniques, and appropriate PPE. These measures significantly reduce the risk of serious injuries on construction sites. Just as importantly, effective training and supervision ensure that safety procedures are consistently followed rather than ignored under pressure. By building strong safety awareness and maintaining high standards, site personnel can protect themselves and their colleagues.