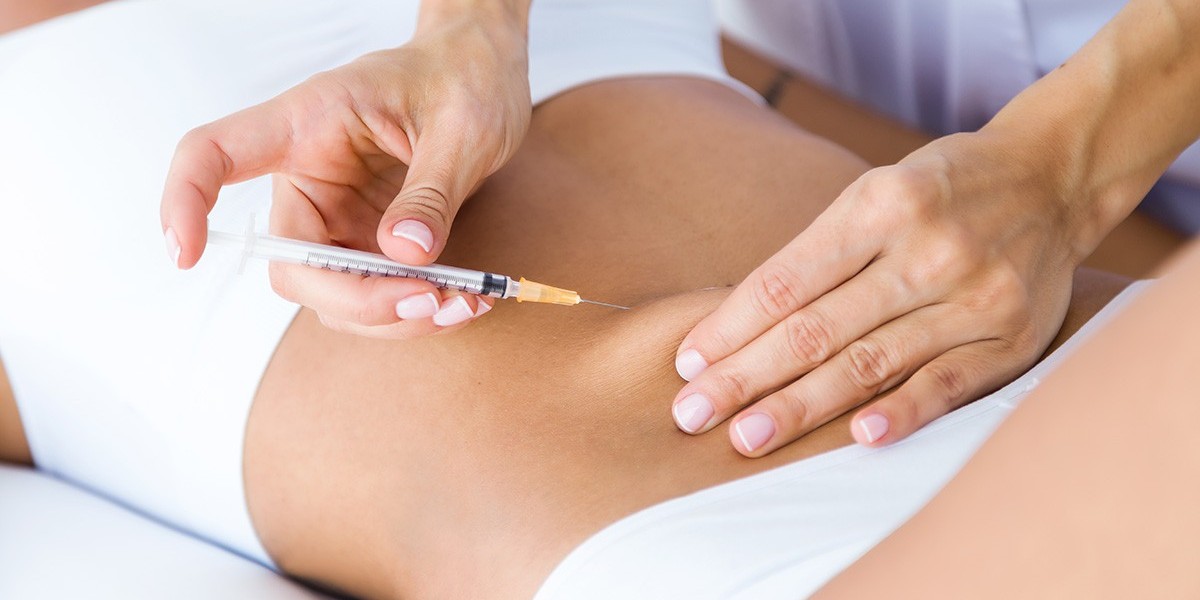
1. What Is Mesotherapy?
Mesotherapy (حقن الميزو) involves multiple microinjections into the mesoderm (the middle layer of skin). For fat reduction, the injected solutions typically contain a combination of:
Lipolytic agents (fat-breaking substances)
Vitamins and amino acids
Enzymes
Plant extracts
Phospholipids
The most studied and commonly used fat-dissolving agents are phosphatidylcholine (PC) and deoxycholic acid (DC).
2. How Mesotherapy Reduces Fat: The Biological Mechanisms
A. Adipocyte (Fat Cell) Disruption
Deoxycholic acid is a bile acid that naturally helps digest dietary fats.
When injected into fat tissue, it disrupts adipocyte cell membranes, causing fat cells to rupture.
The released fat (triglycerides) is broken down into fatty acids and glycerol.
➡️ These byproducts are then processed by the lymphatic system and liver and eliminated through normal metabolic pathways.
B. Enhanced Lipolysis
Some mesotherapy formulations stimulate lipolysis, the metabolic process where stored fat is converted into energy.
Ingredients like caffeine, L-carnitine, and isoproterenol may:
Increase cyclic AMP (cAMP)
Activate hormone-sensitive lipase
Promote fatty acid release from fat cells
This mechanism is more metabolic than destructive and may require multiple sessions.
C. Localized Action
Because injections are placed directly into targeted fat pockets:
The effect is localized, not systemic
It works best for small, stubborn fat deposits (e.g., chin, abdomen, thighs, flanks)
Mesotherapy is not a weight-loss treatment, but a body-contouring approach.
3. Inflammatory Response and Remodeling
After fat cell disruption:
A controlled inflammatory response occurs
Macrophages remove cellular debris
Mild collagen stimulation may lead to skin tightening over time
This inflammatory phase explains common post-treatment effects like swelling and tenderness.
4. Scientific Evidence: What Does Research Say?
Deoxycholic acid has strong clinical backing and is FDA-approved (in a purified, standardized form) for submental fat reduction.
Studies show a permanent reduction in fat cells in treated areas.
Evidence for mixed “cocktail” mesotherapy formulations is less consistent, as:
Ingredients vary widely
Concentrations are not standardized
Protocols differ between practitioners
➡️ Outcomes depend heavily on formulation, technique, and patient selection.
5. Safety and Limitations
Common Side Effects
Swelling
Bruising
Pain or tenderness
Temporary numbness
Potential Risks
Irregular contours if fat is unevenly dissolved
Infection if sterility is compromised
Nerve injury (rare, but possible with poor technique)
Mesotherapy should only be performed by trained medical professionals with a solid understanding of anatomy.
6. Who Is an Ideal Candidate?
Mesotherapy works best for individuals who:
Are close to their ideal body weight
Have localized fat resistant to diet and exercise
Have good skin elasticity
Want gradual, non-surgical improvement
7. Mesotherapy vs. Other Fat Reduction Methods
| Method | Mechanism | Invasiveness | Permanence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesotherapy | Chemical fat cell destruction | Minimally invasive | Permanent fat cell loss |
| Cryolipolysis | Cold-induced apoptosis | Non-invasive | Permanent fat cell loss |
| Liposuction | Physical fat removal | Surgical | Permanent fat cell loss |
Bottom Line
Mesotherapy for fat reduction works primarily by destroying fat cells or stimulating localized fat metabolism through targeted injections. While scientifically plausible and clinically effective for small areas—especially when using well-studied agents like deoxycholic acid—it is not a substitute for weight loss o